I don’t know what’s the matter with people: they don’t learn by understanding; they learn by some other way – by rote, or something. Their knowledge is so fragile!
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman was a Nobel Prize-winning physicist who significantly contributed to quantum mechanics and particle physics. He also pioneered quantum computing and introduced the concept of nanotechnology. As a renowned lecturer, he taught at Cornell and Caltech.
Despite his numerous accomplishments, Feynman considered himself “an ordinary person who studied hard.” He believed that with enough effort, anyone could learn even the most complex subjects, like quantum mechanics and electromagnetic fields. Feynman’s approach to learning emphasized curiosity, persistence, and a deep understanding of fundamental principles.

According to him, what made Richard Feynman remarkable wasn’t innate intelligence but his systematic approach to identifying gaps in his knowledge and then immersing himself in understanding them thoroughly. Throughout his career and life, Feynman shared insights into his process for tackling complex concepts in physics and distilling knowledge with clarity and simplicity. Many of these insights have been compiled into what is now known as “The Feynman Technique.”
The Feynman Technique
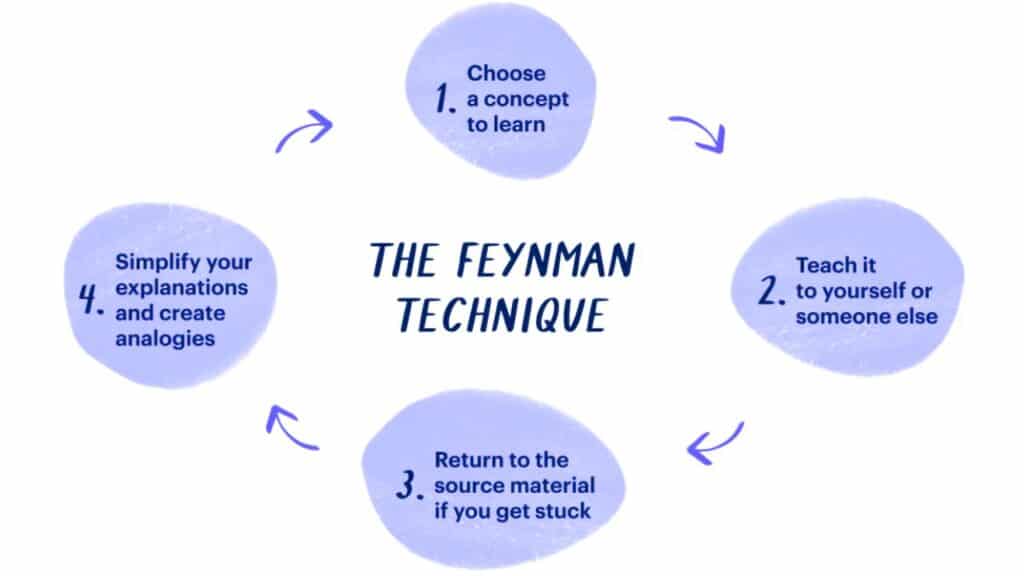
The Feynman Technique involves four key steps:
- Choose a Concept: Identify a topic you want to understand.
- Teach It to a Child: Explain the concept in simple terms, as if teaching a child or someone unfamiliar with the topic.
- Identify Gaps: Find the areas where your explanation falls apart, or you struggle to simplify. These are the gaps in your understanding.
- Review and Simplify: Review your source material to fill in the gaps and refine your explanation. Repeat the process until you can explain the concept clearly.
By using the Feynman Technique, Feynman believed that anyone could learn and understand even the most complex subjects with enough effort and persistence.
Step 1: Identify the Topic
The first step of the Feynman Technique is to choose a specific topic you’ve recently studied or want to test your knowledge on. This can be anything, but make sure it’s narrow enough to explain in under five minutes. For instance, instead of picking “medicine,” choose “the cardiovascular system” or narrow it down further to “Cardiac Cycle.” Selecting a broad topic will make it very difficult for you in the second step.
Learning Benefits:
- Focused Learning: Concentrating on one specific area helps you know exactly what to learn.
- Simplicity: A smaller topic makes completing the Feynman Technique steps easier, reducing the risk of getting overwhelmed.
- Addressing Weaknesses: It forces you to confront and address areas where your understanding is weak.
Action Tip: Write the topic clearly at the top of a piece of paper.
Step 2: Teach It to a Child
Now, explain the topic as if you’re teaching it to a small child or someone without prior knowledge. Use simple language and avoid jargon. For mathematical concepts, include examples to show how they work in practice. When explaining to a small child, imagine you are talking to a 5-year-old.
Learning Benefits:
- Active Learning: Teaching forces you to engage with the material actively, which is more effective than passive methods like rereading or highlighting.
- Immediate Feedback: If you struggle to explain something simply, it reveals gaps in your understanding.
Action Tip: Write the explanation on your paper in your own words, keeping it simple and using examples or analogies.
Step 3: Identify Knowledge Gaps
As you explain the topic, note any points where you struggle or need to refer back to your notes. These are your knowledge gaps. Challenge yourself to break down technical terms into simpler components.
Learning Benefits:
- Targeted Learning: Identifying gaps makes your learning more intentional, focusing on areas that need the most work.
- Iterative Process: Repeatedly teaching and filling in gaps helps encode knowledge into long-term memory.
Action Tip: Mark the difficult areas and note where your explanation needs simplification.
Step 4: Simplify
Finally, refine your explanation. Rewrite it in simpler terms, reorganize your thoughts for a natural flow, and use clearer examples. This step may need to be repeated until you can effortlessly explain the topic.
Learning Benefits:
- True Understanding: Simplifying your explanation ensures you understand the topic deeply.
- Increased Confidence: Successfully teaching a previously confusing topic boosts your confidence and encourages further learning.
Action Tip: Continuously refine your explanation until it’s clear and simple enough for a child to understand. This is how the Feynman Technique for studying turns complex subjects into manageable ones.
By following these steps of Feynman’s technique, you’ll transform your approach to learning, making complex topics easier to grasp and retain. The Feynman method proves that with the right strategy, anyone can master challenging subjects.
How I’m using the Feynman technique as a medical student:
I am a first-year medical student, and medicine is a very hectic field because the individual has to study so much to become a doctor. It is commonly said that only nerds can do MEDICINE lol! As in medicine, there are so many complex topics, whether it is the ANATOMY of Muscles or the PHYSIOLOGY of the Heart. To do it effectively, the only method helping me is the FEYNMAN TECHNIQUE; believe it or not, I’m trying to implement feynman technique on every topic I study. I can say that you will get the most out of your studies once you do it by following this method.
Pingback: active recall study technique - Sami Qamar